AcidA substance which donates H+ (proton) to other substances.
A process which occurs in the presence of oxygen.
 That which is hot and moist. Alchemical air symbolizes daring and skill. In this book Air speaks for skepticism and honesty.
That which is hot and moist. Alchemical air symbolizes daring and skill. In this book Air speaks for skepticism and honesty.
A substance which accepts H+ (proton) from other substances. An alkali reacts with water to produce OH- in solution.
A process which occurs in the absence of oxygen.
An alkali.
A procedure by which the bejeezus is driven from a substance, often by intense heat.
An agent which speeds up a reaction. A catalyst is not consumed in the reaction it catalyzes and so does not appear as a reactant or product in the balanced chemical equation.
A process by which a material combines with oxygen, usually releasing heat.
A pure substance which can be decomposed into two or more other pure substances.
A reaction in which two molecules join together, spitting out a small molecule, usually water, in the process.
A generalization of the observation that the mass of a sealed container does not change.
A procedure by which one substance is dissolved in another to form a solution.
A procedure by which the bejeezus is collected and isolated.
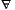 That which is cold and dry. Alchemical earth symbolizes wealth and bounty. In this book Earth speaks for business and industry.
That which is cold and dry. Alchemical earth symbolizes wealth and bounty. In this book Earth speaks for business and industry.
A substance which dissociates into ions when dissolved. Because these ions are free to move about, an electrolyte solution conducts electricity.
A pure substance which has never been decomposed into two or more other pure substances.
A relationship between two things which are equal. In a chemical equation, the two things must have the same number and kinds of elements. In a mathematical equation, the two things must have the same units.
A procedure for making an observation which will be consistent with only one of two or more theories.
A procedure by which one substance is converted to another by decay, often by the action of microorganisms.
 That which is hot and dry. Alchemical fire symbolizes mastery and will. In this book Fire speaks for basic research and experimentation.
That which is hot and dry. Alchemical fire symbolizes mastery and will. In this book Fire speaks for basic research and experimentation.
A symbol, e.g. H2O, used to denote the relative amounts of elements in a pure substance.
The section of the book you are reading right now.
Matter whose composition varies from one place to another within a sample.
Matter whose composition does not vary from one place to another within a sample.
A compound which does not contain carbon. There are exceptions to this definition; carbonates, bicarbonates, and carbon dioxide are generally considered as inorganic compounds.
A process by which water is passed over a solid, taking with it any soluble materials.
A unit of culture which is replicated through imitation. Successful memes exhibit fidelity, fecundity, and longevity. Synonyms include I-dea, inspiration, and spirit.
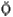 That which flees the fire, descending from heaven to earth. Alchemical mercury symbolizes the spirit and takes its name from the element mercury, which may be distilled without leaving any ash. In this book Mercury provides the motivation for the Sulfur and Salt.
That which flees the fire, descending from heaven to earth. Alchemical mercury symbolizes the spirit and takes its name from the element mercury, which may be distilled without leaving any ash. In this book Mercury provides the motivation for the Sulfur and Salt.
A procedure by which two substances exchange anions or cations.
A compound which contains carbon. There are exceptions to this definition; carbonates, bicarbonates, and carbon dioxide are generally considered as inorganic compounds.
A half-reaction in which electrons appear as products.
A measure of the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution. Solutions with pH less than 7 are acidic, which those with pH higher than 7 are alkaline.
A procedure by which a solid falls out of a liquid solution.
A procedure for purifying a substance by precipitating a solid from a liquid.
The number in front of each substance in a balanced chemical equation.
A question involving the relative weights of reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
Homogeneous matter whose composition is fixed.
A half-reaction in which electrons appear as reactants.
 That which remains from the fire, neither rising to heaven nor descending to earth. Alchemical salt symbolizes the body and takes its name from those salts which are extracted from ashes. In this book Salt provides instructions for making or doing something.
That which remains from the fire, neither rising to heaven nor descending to earth. Alchemical salt symbolizes the body and takes its name from those salts which are extracted from ashes. In this book Salt provides instructions for making or doing something.
A procedure by which one substance is separated from another. Examples of separations include recrystallization, distillation, and chromatography.
The less abundant component of a solution.
Homogeneous matter whose composition is variable.
The more abundant component of a solution.
A procedure for purifying a substance by precipitating a solid from a gas.
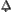 That which is consumed in the fire, rising from earth to heaven. Alchemical sulfur symbolizes the mind and takes its name from the element sulfur, which burns without leaving any ash. In this book Sulfur provides the chemical concepts needed to understand the Salt.
That which is consumed in the fire, rising from earth to heaven. Alchemical sulfur symbolizes the mind and takes its name from the element sulfur, which burns without leaving any ash. In this book Sulfur provides the chemical concepts needed to understand the Salt.
A logically consistent set of principles which account for, explain, or render intelligible a set of observations.
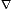 That which is cold and moist. Alchemical water symbolizes belief and foresight. In this book Water speaks for theory and prediction.
That which is cold and moist. Alchemical water symbolizes belief and foresight. In this book Water speaks for theory and prediction.
 Table of Contents for Caveman Chemistry: 28 Projects, from the Creation of Fire to the Production of Plastics
Table of Contents for Caveman Chemistry: 28 Projects, from the Creation of Fire to the Production of Plastics Table of Contents for Caveman Chemistry: 28 Projects, from the Creation of Fire to the Production of Plastics
Table of Contents for Caveman Chemistry: 28 Projects, from the Creation of Fire to the Production of Plastics